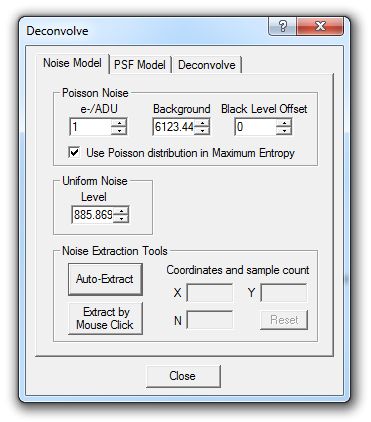
The Noise Model tab initializes the noise model used by deconvolution. The noise model helps determine how strongly to deconvolve different parts of the image. Areas that are mostly noise are not deconvolved as strongly so as to prevent noise amplification; the algorithm will preferentially work on areas of the image that contain information.

The Poisson Noise distribution is required when using the Lucy-Richardson method, and is recommended when using the Maximum Entropy method on images from high-performance cooled CCD cameras; in the latter case, you must check Use Poisson distribution in Maximum Entropy. The e-/ADU (photoelectrons per ADU) setting is used to indicate the CCD camera gain, and is required because Poisson noise statistics are based upon photon shot noise. The value for e-/ADU is set automatically from the EGAIN keyword in the FITS header, if present, or can be entered manually or using the Photons Wizard, which helps determine the proper setting for your camera. The Background field is set just below the average background level in the image. The Black Level Offset specifies the value of any offset that was added to the image before deconvolution, and is set automatically to the negative of the value of the PEDESTAL keyword in the FITS header, if present. Otherwise set it to 0 for raw images or 100 if the image was calibrated in MaxIm DL.
The usual choice for the Uniform Noise Level is the standard deviation of the pixel values in a part of the image that contains no detail. This value is required when using the Lucy-Richardson method.
Click Auto-Extract to automatically determine the correct settings for Background and Uniform Noise Level. Alternatively, you can extract these values from the image manually using Extract by Mouse Click. When this button is pressed, you can use the mouse to select one or more regions, each the current size of the aperture (innermost circle of the mouse rings cursor) where the background level is to be measured. (Right-click on an image to change the aperture size via the standard context menu .) Point the mouse to a dark area of the image which contains no detail, then click. If more than one area is selected the results are averaged; red marker circles are left to indicate the region(s) that you have sampled. X and Y show the coordinates of the most recent area sampled, and N shows the number of areas included in the measurement; you can click Reset to start over.
You can sample the noise statistics from any open image. Normally you will want to sample from the image you are about to deconvolve, but in special cases you might choose to obtain the noise statistics from a different one. Just click on the title bar or image tab of the desired image before clicking Auto-Extract or Extract by Mouse Click.